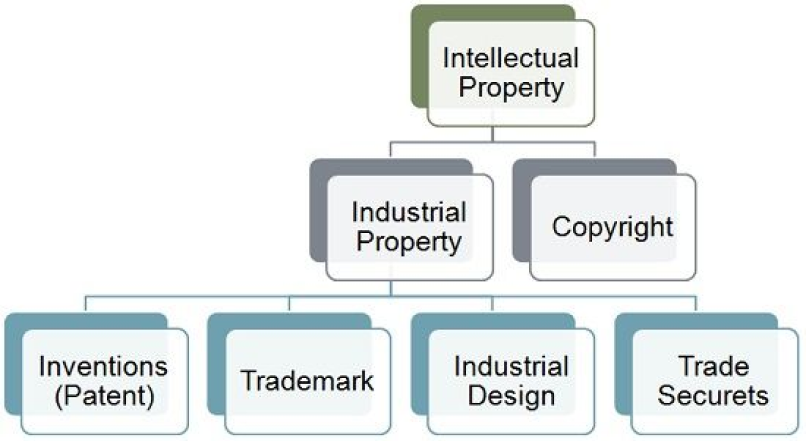
Intellectual property rights (IPR) refer to the legal rights that creators, inventors, and innovators have over their creations or inventions. These rights provide exclusive rights to the creators for a certain period, allowing them to benefit from their work financially and control how it's used by others.
IPR laws vary from country to country, but they generally aim to balance the interests of creators with the public interest in promoting innovation, creativity, and competition. Violating someone's intellectual property rights can result in legal consequences, such as injunctions, damages, or even criminal penalties in some cases.
Our expertise extends to navigating the complexities of cyber law, including resolving domain name disputes and addressing intellectual property issues in emerging sectors such as software, internet, entertainment, and manufacturing industries. We provide strategic counsel to clients on the enforcement and protection of intellectual property rights, including trademarks, copyrights, and patents.
Our seasoned team is adept at handling diverse projects across multiple sectors, including manufacturing, technology, chemistry, life sciences, engineering, and business methods. From drafting and filing to prosecuting and defending intellectual property rights through all phases, We are committed to delivering tailored solutions and safeguarding our clients' innovative assets.